25 powerful methods in JavaScript
⇩
💭 Why this thread?
⬘ Are you learning JavaScript? Even if you are experienced, do you ever feel exhausted by the presence of so many methods?
⬙ The best approach to getting familiar is to know the use cases for these.
Here are 25 methods. Let's discuss their use cases.
The methods are,
➤ Array.prototype's
➊ forEach()
➋ map()
➌ reduce()
➍ every()
➎ filter()
➏ find()
➐ slice()
➑ splice()
➒ push()
➓ pop()
➊➊ shift()
➊➋ unshift()
➊➌ indexOf()
➊➍ findIndex()
➊➎ sort()
➤ String.prototype's
➊➏ toLowerCase()
➊➐ toUpperCase()
➊➑ substring()
➊➒ indexOf()
- charAt()
➋➊ trim()
➤ Math's
➋➋ floor()
➋➌ random()
➤ Global Methods
➋➍ setTimeout()
➋➎ setInterval()
➊ Array.prototype.forEach()
➤ Use Case
✔ To iterate through each element in the array
✔ Perform a task on each element
✘ Not suitable if the task is supposed to return some value
✩✩ forEach() is also available in Set.prototype and Map.prototype
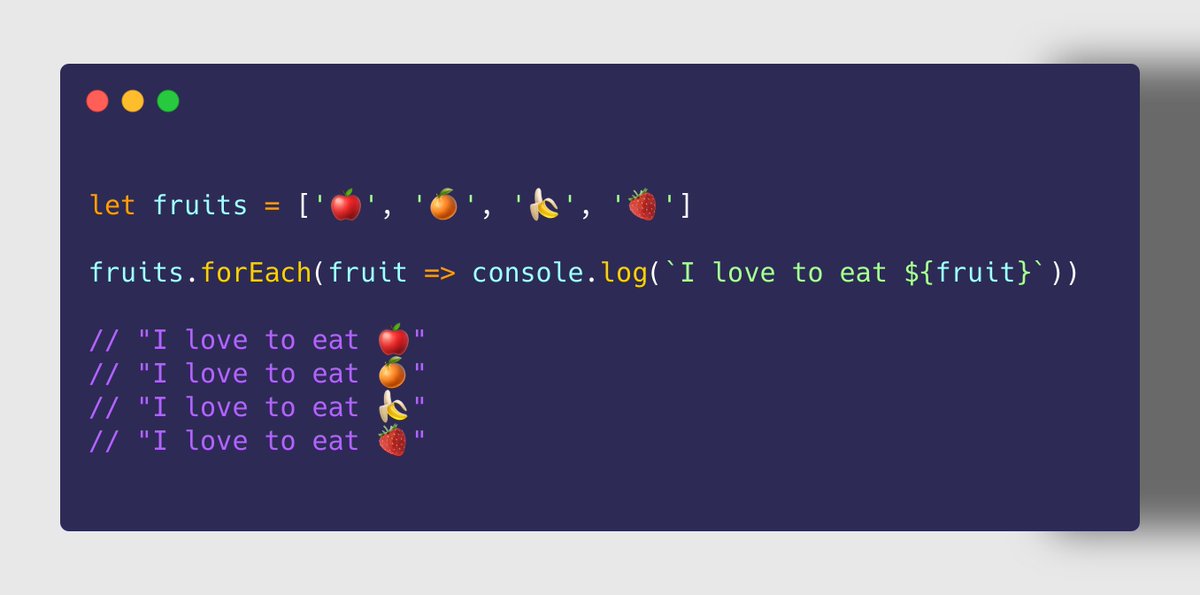
➋ Array.prototype. map()
➤ Use Case
✔ To iterate through each element in the array
✔ Perform a task on each element which returns a value
✔ Returns a new array with all returned values
✘ Not suitable if the task doesn't return any value

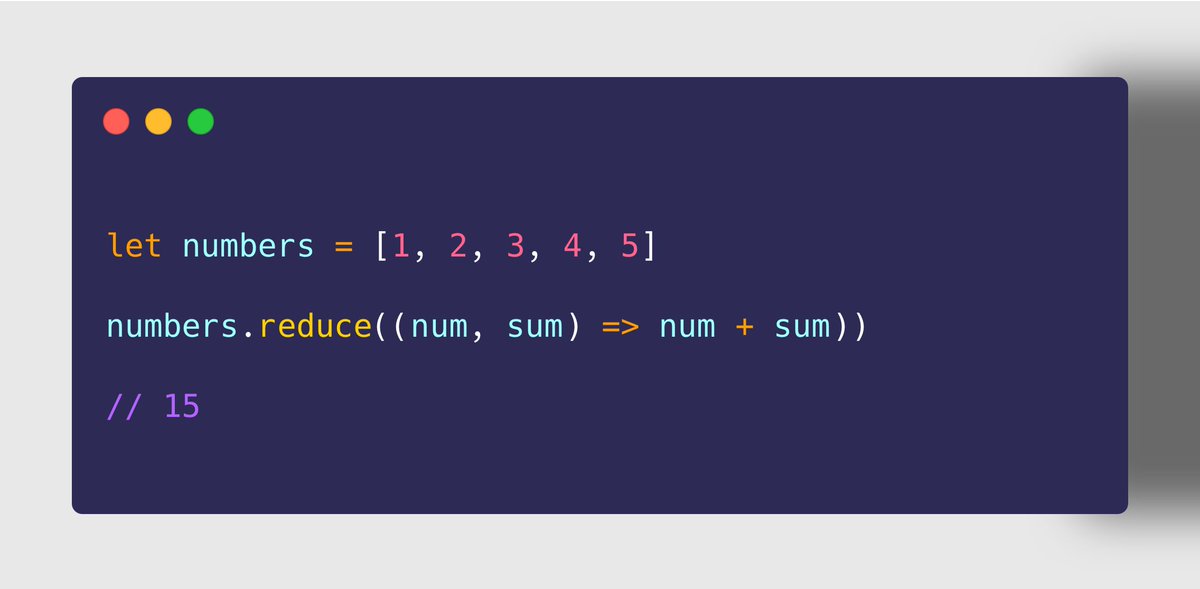
➌ Array.prototype.reduce()
➤ Use Case
✔ To iterate through each element in the array
✔ Perform a task on each element which accumulates the previous returned value with current element to return a new value
➤ Example
➀ Sum of all items ➁ Max of all items
➍ Array.prototype.every()
➤ Use Case
✔ To iterate through elements in the array until a certain condition is not met
✔ The task performed on each element must return a boolean value
✘ Stops iterating when condition is not met. Hence, it's not suitable for skipping.

➎ Array.prototype.filter() ➏ Array.prototype.find()
➤ Use Case
✔ To find element(s) which match a criteria
✔ Use find() to find the first matched element
✔ Use filter() to find all matched elements
✩✩ filter() returns a new array of matched elements

➐ Array.prototype.slice()
➤ Use Case
✔ To fetch a sub-array from a larger array
✩✩ slice() returns a new array, doesn't modify the existing array

➑ Array.prototype.splice()
➤ Use Case
✔ To replace a portion of the array with new elements
✩✩ splice() modifies the existing array

Array.prototype's ➒ push() ➓ pop() ➊➊ shift() ➊➋ unshift()
➤ Use Case
✔ Use push() and pop() to insert/remove elements from the end.
✔ Use shift() and unshift() to insert/remove elements from the start.
✩✩ These methods modify the existing array

Array.prototype's ➊➌ indexOf() ➊➍ findIndex()
➤ Use Case
✔ To find the index of the first matched element
✔ indexOf() does exact match (===)
✔ findIndex() allows for custom match

➊➎ Array.prototype.sort()
➤ Use Case
✔ To sort all elements of an array in some order
✔ Provide a comparator to define custom order
✔ By default sorting order is lexical
✩✩ This method modifies the existing array

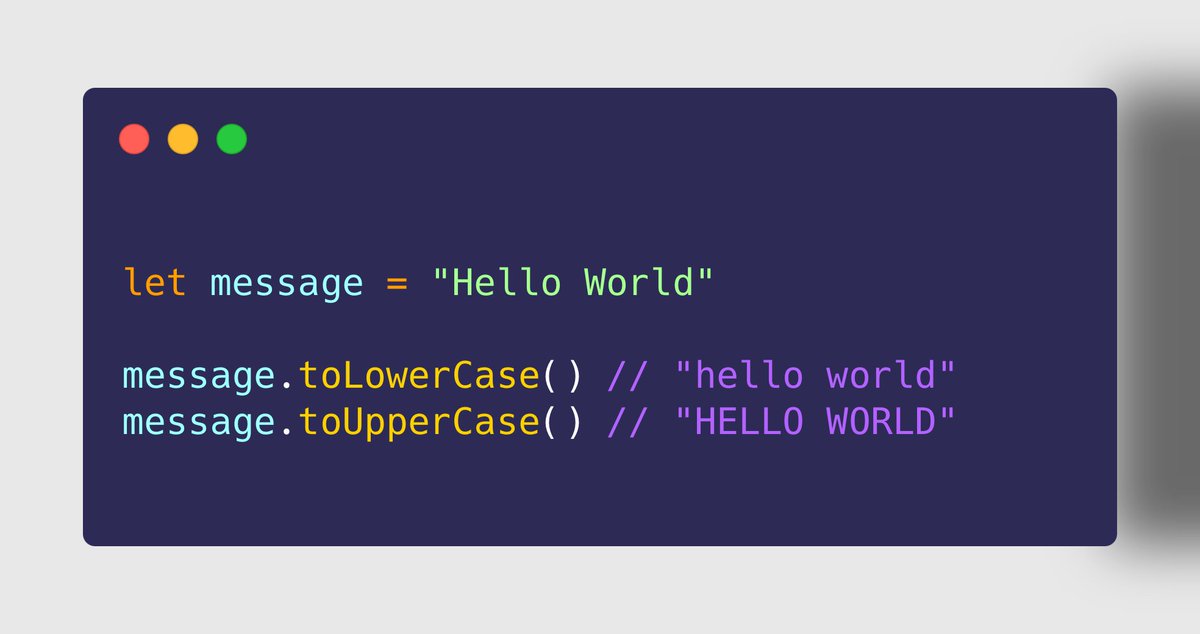
String.prototype's ➊➏ toLowerCase() ➊➐ toUpperCase()
➤ Use Case
✔ To convert entire string to lowercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()
✔ To convert entire string to uppercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()
✩✩ These methods returns a new string
➊➑ String.prototype.substring()
➤ Use Case
✔ To fetch a part of the string between 2 indexes
✩✩ substring() returns a new string

➊➒ String.prototype.indexOf()
➤ Use Case
✔ To find the very first occurrence of a "substring" in the original string
✔ We can also mention from which index the occurrence should be checked

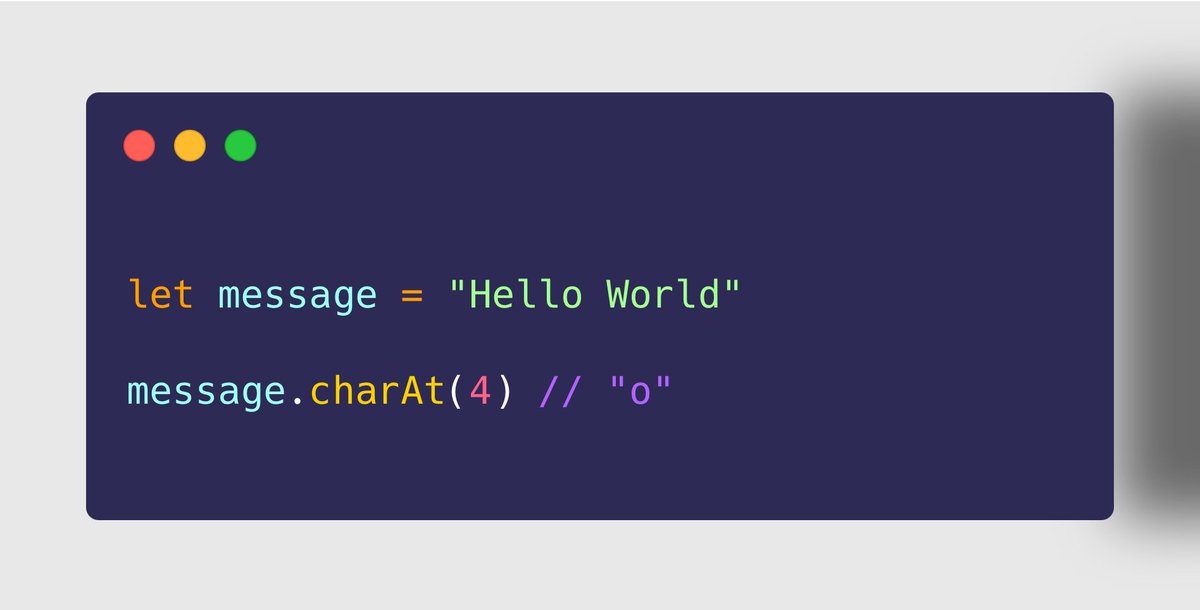
- String.prototype.charAt()
➤ Use Case
✔ To fetch the character at a specific position of a string.
✔ The character fetched is in UTF-16 and returned as a string.
➋➊ String.prototype.trim()
➤ Use Case
✔ To remove whitespace from both ends of a string
✩✩ trim() returns a new string

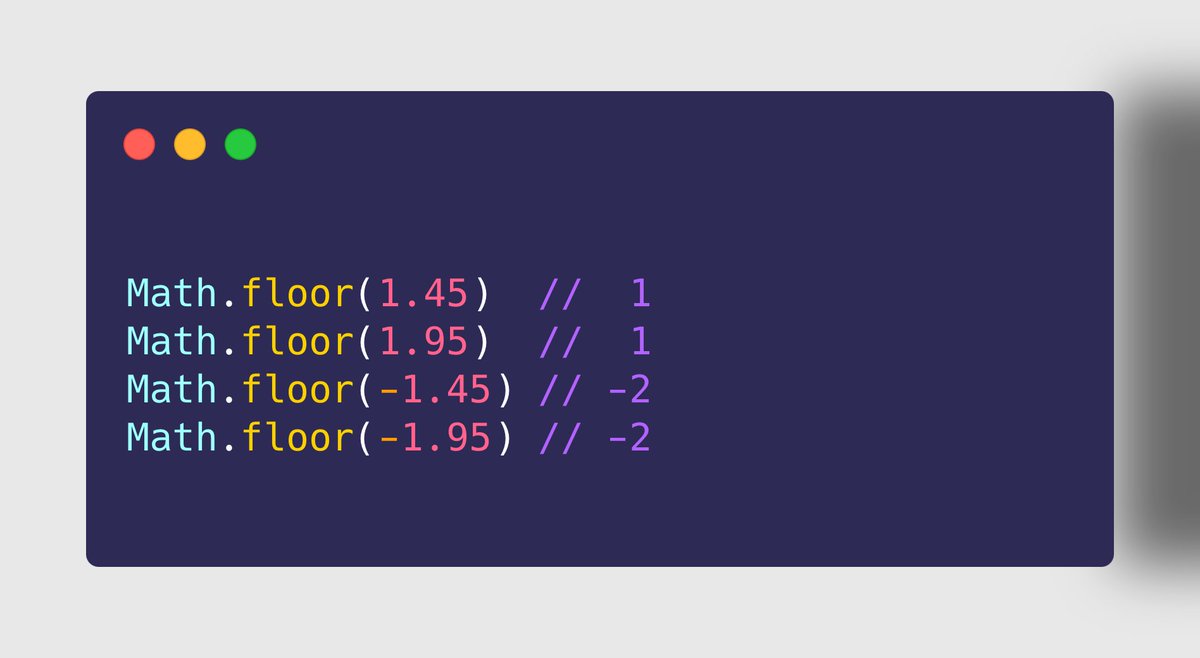
➋➋ Math.floor()
➤ Use Case
✔ To get the largest integer less than or, equals to the given number
➋➌ Math.random()
➤ Use Case
✔ To get a floating-point pseudo-random number in the range of 0 to less than 1
✔ It can be multiplied by any number to make a random number being generated in the range of 0 to less than that number

➋➍ setTimeout()
➤ Use Case
✔ To execute a function or, piece of code after a timer expires
✔ The code is executed only once.
✘ It is an asynchronous function. It shouldn't be used where pausing of execution is intended.

➋➎ setInterval()
➤ Use Case
✔ To execute a function or, piece of code repeatedly with a fix time delay
✘ The code is ensured to be executed each time after the time delay. But not "exactly" after the time delay.
✩✩ Cancel further execution using clearInterval()

💭 Tasks for you
Find use cases of below
➤ String.prototypes's
❍ startsWith() / endsWith()
❍ fromCharCode()
❍ padStart() / padEnd()
❍ repeat()
❍ match() / matchAll()
❍ replace() / replaceAll()
➤ Math's
❍ ceil()
❍ trunc()
❍ round()
Hey 👋
I am a Tech Educator from India 🇮🇳
I am sharing Tutorials, Tips, Infographics, Cheat Sheets, Practice Questions, Project Ideas and Roadmaps on Web Development, DSA and, Database.
To never miss anything, Follow Me ✅
100% of Profits Are Donated To Research-Backed Charities.